Search engine optimisation (SEO)
 SEO is the practice of improving a website's position with search engines like Google. The purpose of SEO is to ensure that when a web user searches for a particular keyword or phrase that your web pages will be shown to those users. However, Google has implemented many changes to the way they index websites in recent years, impacting web and content managers and their search engine ranking.
SEO is the practice of improving a website's position with search engines like Google. The purpose of SEO is to ensure that when a web user searches for a particular keyword or phrase that your web pages will be shown to those users. However, Google has implemented many changes to the way they index websites in recent years, impacting web and content managers and their search engine ranking.
The key point in all of these changes is relevancy. In this sense it refers to what is relevant to the person visiting a website.
It is best practice to always consider the user. Attempting to trick search engines like Google will most likely lead to poor results for your web pages.
There are a number of ways that web publishers can assist search engines to properly index your web pages. These are outlined below.
Page titles
This is the first thing a user sees when conducting a search. They also appear as tabs at the top of the web browser. Best practices for page titles include:
- Create short but descriptive titles – no more than approximately 55 characters.
- Relevant to the page content – Ensure the title reflects the content of the page
- Each web page title should be unique – Avoid copying titles to save time
Metadata keywords
Metadata keywords are a specific type of meta tag that appear in the HTML code of a web page and alert search engines to the main topic(s) contained within the content of a web page. The keywords used also reflect any words or phrases that users may use to search for the web page.
Description metadata tag
The Description metadata tag is only visible to users on the search engine results page. (See image below for example.)
Descriptions allow the web or content manager to control what a user sees on the results page. If you do not include a description meta tag, Google will display the first 150-160 lines of text.
- Limited to 150-160 characters. Text will truncate after this limit.
- Relevant descriptions – Ensure the description is relevant to the page content
- Each description should be unique – Avoid copying descriptions to save time.
Content
Content includes text, images, videos, podcasts and more. For most web publishers it is the text that will be most important to get right.
- Write content for the web page users – Think about how you can best write and lay out the content for your users. You want them to easily navigate and find content on your site.
- Remain on-topic – Once again relevancy is the key here. Does the content make sense to a user? Does the content match the page title, description and headings?
- No dirty tricks (known as black hat SEO). This includes link building, peppering keywords and hiding text by making the colour the same as the background. These and many other poor web practices will likely lead to low rankings with search engines.
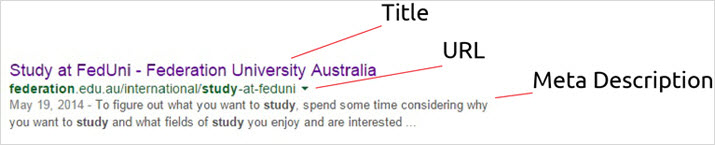
URL
The Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is the text under the title on the search engine results page.
When you create a page title the URL, or web address, is automatically created. When creating the URL consider:
- Relevancy to titles descriptions and page content
- URLs can contain 2083 characters, however it is better to keep shorter where possible.
- Use hyphens to separate words like this: federation.edu.au/international/study-at-feduni.
Headings
Headings enable you to lay out your content appropriately for users to easily read and navigate through your page content. <h> tags usually provide a hierarchy of headings that you can use on your web page. Where possible you should:
- Us the <h1> tag as the title of the page and not use it elsewhere.
- You can use other heading tags such as <h2>, <h3> and so on as often as needed.
- Ensure the text inside <h> tags is relevant and suggests what is to follow.
Anchor text
Anchor text, or link text, is the text used when creating a hyperlink on a web page. Often you will want to create a link on your web page to other content on your website or on another website. When creating links consider:
- Relevancy of the text – it should make sense to a user
- Use short and descriptive text - eg, Browse our Course Finder
- Avoid using terms like 'click here', 'read more'.
To learn more about SEO view Google's SEO Starter Guide (pdf, 4.2mb)
